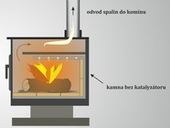
The object of article is to provide basic information about approaches to testing of stoves burning solid fuels in Europe and some other countries. Generally, stoves in Europe are tested according standard EN 13240. However, there’re other standards on national basis, for example Norwegian standards NS3058 and NS3059. If we look away from European border we can found standards which describe methods of stove testing – Australian/New Zealand standards and EPA standards in U.S.A. The article provides information about measuring sets, characterization of used fuels, testing categories for burning periods, measured parameters, emission limits and others things which are in these standards.
Archiv článků od 11.6.2013 do 13.1.2014
Biomass Action Plan envisages the available space in 3 variants with respect to the degree of self-sufficiency in food C.R. Area of fast-growing tree species growing steadily, in terms of total energy production is negligible involvement. By registering, according to the law of ash can be removed from the category of waste, and consequently can be applied as fertilizer.
The object of article is to provide basic information about approaches to testing of stoves burning solid fuels in Europe and some other countries. Generally, stoves in Europe are tested according standard EN 13240. However, there’re other standards on national basis, for example Norwegian standards NS3058 and NS3059. If we look away from European border we can found standards which describe methods of stove testing – Australian/New Zealand standards and EPA standards in U.S.A. The article provides information about measuring sets, characterization of used fuels, testing categories for burning periods, measured parameters, emission limits and others things which are in these standards.
Plans of the coalition in energy sector:
- - Reduce energy intensity of industry
- - Diversification of energy resources
- - Reduce energy performance of buildings
- - Review the RES support
- - Support for the research of RES and energy storage
- - Construction of new units at Temelin Nuclear Power Plant
- - Reconstruction and greening of heating industry
- - Assure coal for heating
- - Revitalization after the coal mining
- - Support for Smart Grids
This article describes a photovoltaic generator used for water heating and compares it with the well known solar thermal system. Photovoltaic modules can be connected to the load both directly or via a regulator that tracks the maximal power point of the modules. Measurements and simulations in meteorological conditions of Czech Republic were done to set the energy loss for a system without the regulator. It was found that without the regulator the system can deliver maximally 77 % of energy. To achieve high efficiency of the system, maximal power point tracking has to be used.
The market for wood pellets has grown, which is understandable due to the following market growth with boilers and biomass stoves. On the contrary, the market for agro pellets gradually declining. Pellets from agricultural production are completely different type of fuel than wood pellets. These industrial fuel which is in most cases not suitable for domestic heating.
Thin-walled composites made of fine-grained cement-sand matrix reinforced by alkali-resistant glass fibres are currently used for the range of applications in the building industry, especially as architectural elements and cladding panels. Their advantage is mainly low weight as well as resistance to mechanical and weather impacts. These preconditions led to an innovative solution of cladding elements for accumulation and consecutive utilization of solar energy. Solar energy is transformed into heat energy by the means of an integrated pipe system and the heat achieved is deposited by the means of a heat water reservoir. Element surface can be set with photovoltaic cells. This material is possible to use as a roof panel as well. On the contrary to standard robust photovoltaic panels a difficult superstructure is not necessary and roof structure assembling is much easier. A wide range of simulation trials in interior as well as real tests in exterior was carried out with cooperation of a renowned company from the photovoltaic branch.
The article is a commentary on Czech TV report about the feasibility of reducing CO2 in the atmosphere. To eliminate carbon dioxide from the atmosphere has been proposed a number of methods, many of which are currently at the stage of mere concept. Namely, this includes the artificial trees mentioned in the report. Even if such methods work, there still remains the question of what to do with the captured CO2. Storage in geological formations is uncertain and material recovery faces high energy demands. In some cases there is a misunderstanding resulting from the confusion of CO2 and other emissions. Namely on the facade, which allegedly eliminate CO2 from the air, but in fact it eliminates nitrogen oxides. The only reliable way to reduce CO2 emissions permanently is to reduce energy consumption.
Solar radiation can be utilised in two basic ways. You can either gain heat from solar thermal collectors or electricity in photovoltaic panels. So far, heating of water by photovoltaics was too expensive to compete with conventional solar thermal collectors.
Weight , durability , and currently even the price of solar thermal collectors is comparable with commercially available photovoltaic modules.
Annual energy yield per unit area is approximately twice in the solar thermal collectors compared to the highest quality photovoltaic modules with cells made of monocrystalline silicon, due to the higher efficiency.
In the summer the photovoltaic modules are better when the working fluid is heated to temperatures above 100 °C. In the winter the breaking point is about 40 °C. The advantage of photovoltaics is the absence of heat transfer fluid and easier transfer of energy produced to the point of use. Electricity can also be used more versatile than heat.
If the investment cost of a complete solution of heating water by electricity from photovoltaic panels, either directly or using a heat pump, is lower than the investment cost of the solar thermal system, the PV water heating can be considered as effective utilization of electricity from photovoltaic plants. Such a solution could then be included as an alternative to any grant support for solar water heating.
The joint program to promote the replacement of boilers is spreading to various regions of the Czech Republic. The aim is to reduce subsidies to air pollution from small combustion plants using solid fuels. Refers to the local heating of the heat output of 50 kW. The subsidy is provided to the various types of boilers and applies only to the replacement of existing manually filled with solid fuel boilers with new efficient low-emission sources.
It is much more efficient to produce mechanical work by electrical engine "fuelled" by photovoltaic modules than produce the same amount of mechanical work by internal combustion engines running on fossil fuel or first-generation biofuel. The first choice could be much cheaper and produce order of magnitude more energy from agricultural land than biofuels. Therefore photovoltaics could hypothetically contribute significantly to the fulfillment of national and European target for the share of renewable energy sources (RES) in transportation.
The Chamber of Deputies approved the stopping of subsidies (feed-in-tariff) for renewable energy sources beginning January 1 2014. Support for combined heat and power generation from fossil fuels and support combustion of waste based on the same legislation remained unchanged.
By the opinion of the Chamber of RES the provisions of the law requiring a proof of beneficiaries structure is insufficient "especially because it does not apply to owners up to 10% of the shares and efficiency is only proposed from 1 July 2014, which gives a disproportionately large space to conceal the ownership structure."
The thermoelectric transformation of waste heat into electric power is considered to be a promising technology enabling to enhance electric efficiency of current energy processes, fuel saving and emissions reduction. The submitted paper deals with the construction of thermoelectric generators, current thermoelectric applications and their potential utilization.
Recently broad media in the Czech Republic coverage on hazards from PV systems to fire fighters. Similar situation was in Germany two years ago. That is why Fraunhofer-Institut für Solare Energiesysteme ISE together with TÜV Rheinland and other partners implemented a research project „Assessment of fire risks in PV systems and development of safety concepts for risk mitigation“. The project concluded that the fire risk of PV system is much less than it is publicly alleged in Germany.
There is a small risk that fires can be started by PV components. This risk can be reduced by careful installation, initial verification i.e. inspection and testing, periodic verifications, (yield) monitoring to detect degradation problems, and verification of test procedures and maintenance requirements for conventional AC- components. Overall conclusion is that PV systems are not maintenance free.
Whole presentation from EU PVSEC (in English).
The potential of microalgae as a source of renewable energy received lately large attention. Microalgal biomass is a potential source of renewable energy and it can be converted into energies such as biodiesel, ethanol, combustible gasses or it can be used to produce pharmaceutical, food additives and other. If microalgal biofuel production is to be sustainable and economically acceptable, further optimization of microalgae production and its conversion to viable compounds is needed. Microalgae are photosynthetic microorganisms with simple growing requirements (light, sugars, CO2, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) that can fixate CO2, produce lipids, proteins and carbohydrates in very short periods of time.
These products can be processed into both biofuels and valuable co-products. Municipal, agricultural and industrial wastewaters are able to satisfy growing requirements of microalgae and hence provide cost-effective sustainable biofuel production with simultaneous wastewater treatment. Integration of biofuel production and wastewater treatment has major advantages for both industries, however major challenges needs to be overcome in order to implement such facilities in large-scale. This paper reviews current status of this topic with focus on fuel production with simultaneous algae wastewater treatment and major technological challenges.
The emissions trading scheme, EU's flagship climate policy tool, is at a turning point. With the price of carbon hovering way below €5 per tonne and a glut of permits on the market, something must be fixed or the instrument will turn to dust. As a first step towards correcting the problem, the European Commission has proposed a measure to withhold pollution permits temporarily, a process called ‘back-loading'. Back-loading appears harmless enough as all withheld allowances would re-enter the market before the end of this decade. Therefore the European Commission and many stakeholders recognise that structural measures are needed so that the ETS would support the transition towards a low-carbon economy.
List of all companies that offer recycling of photovoltaic modules in the Czech Republic is included. Already 9 companies is on the list, of which 4 already received marketing authorization, 5 more likely to gain the authorization in the coming days. Contract can be concluded even with a company that has not received the marketing authorization yet.
In order to assess the diffusion rate of solar and wind power plants in the Czech residential sector, we analyse data on licenses for business in the energy industries. We arbitrary set the maximum installed capacity for installations on residential roofs on 10 kWe and find out that the current number of such installations corresponds to 0.5 % of inhabited family houses in the Czech Republic, with most installations being in the Pilsen region and least in the Karlovy Vary and Liberec regions.
When compared with the overall development of solar power plants, it shows that the installations of up to 10 kWe accounted for about 35 % of all the solar power plant installations, but only for 1.9 % of the total installed capacity. Micro wind turbines are up to now not very expanded; we found only 20 installations of micro wind turbines.
Recycling of PV modules in the Czech Republic is not guaranteed despite of that four companies offer the recycling already. Besides two (specialised to recycling of PV modules) subsidiaries of traditional recycling companies, third traditional recycling company cooperate with PV Cycle, and fourth company was recently established by ten stakeholders including Czech Photovoltaic Industry Association and some large operators of PV power plants. Czech legislation does not guarantee that collected money will be available when recyclation will occur.
zpět na aktuální články