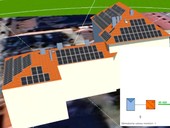
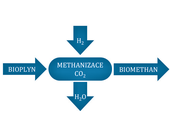
The first newly built agricultural biomethane station in the Czech Republic is in operation in Krakořice near Šternberk in the Olomouc Region. It will produce approximately 2 million Nm3 of biomethane annually, which will cover the consumption of approximately 1,500 households.
Archiv článků od 1.8.2021 do 28.5.2025
This article presents a simulation analysis conducted at the Institute of Environmental Engineering at CTU, as part of the international exercise IEA EBC Annex 82. The aim of the joint exercise, which involved more than ten international research teams from different sectors, was to test and compare different approaches towards achieving energy flexibility in buildings on the basis of a unified exercise assignment. The Czech team based its study on a comprehensive simulation of the energy behaviour of buildings, including a detailed numerical model of the heating, hot water preparation, cooling and ventilation systems. The model was used to study the building potential for providing energy flexibility and future responsibilities of building operators in the context of smart energy grids.
Example of the Design of Thermal Collectors for the Domestic Hot Water Preparation in a Family House
It is possible to design solar energy systems (SES) with solar collectors in several ways: manually - by calculation; using software - there are several calculation programs for SES design, e.g. T*Sol from the renowned German company Valentin software for the calculation of thermal heat collectors, or PV*Sol for the design and simulation of photovoltaic power plants of any size; or according to the manufacturer's instructions - if we know the manufacturer/supplier of the equipment when designing the SES, we can use the recommended calculation procedures from the design documents of the given company, provided that they are available.
The paper presents soft densification as a phenomenon suitable for the sustainable development of ageing suburban housing of larger cities in the Czech Republic. The background, potential, and risks are described using literature and foreign practical experience and suggest the possible application of this strategy in Czech conditions. A description of the spatial types of soft densification regarding the reserves of existing land and houses, and a description of the main actors of the phenomenon serve as a basis for further research. The article also includes an introduction of the online database of Dense Satellites, which was created to collect good practice projects and popularize the topic among the wider public.
The article presents a project submitted by TAČR in the Environment for Life section 2. The goal of the project is to find the application of recycled glass fractions from photovoltaic panels in the field of construction. The project focuses on three basic silicate building materials, which are able to incorporate glass recyclate shards into their structure during the hydration, firing and melting process. The paper specifies the first results of testing possibilities for use of glass recyclate from photovoltaic panels for concrete masonry units. It compares particular recipes and its physical and mechanical properties with the main focus on the compressive strength. It then compares the values of these recipes with the values of commonly used composite materials for masonry units without recyclates.
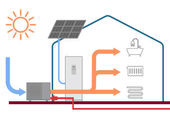
The design of a photovoltaic system taking into account heat loss, external and internal gains, the method of heating and water heating is made possible by a calculation tool created for the balancing of buildings with photovoltaic systems. In the example, combinations of FS with a heat pump or with an electric boiler are compared.
Starting from January 1, 2023 (in the Czech Republic), on the basis of § 4, paragraph 1 of Decree No. 264/2020 Coll., on the energy efficiency of buildings, it is necessary for buildings or zones with cooling, humidity control or electricity production to calculate the energy efficiency of the building with an interval of one hour. The subject of the article is an approximation of the basic specifics of the hourly step of calculation and a comparison of the results of the calculation and the assessment of energy intensity in the monthly and hourly step of calculation according to the requirements of the applicable legislation.
This post discusses the possibilities of using green walls and their impact on the living environment, micro-climatic conditions and the overall perception of comfort in the interior. Green walls, or vertical gardens, are a desired architectural element of spaces, whether external or internal, for their aesthetic value and significant ability to favorably influence the environment in which we live. Vertical gardens improve acoustics, humidify, freshen and cool the air, capture dust and clean the air. The green wall also functions as a very effective heat and sound insulation system. Any larger green area fundamentally increases the quality of the microclimate, and therefore also people's lives.
Within the project, a new concept of a combination of a constructed wetland and an extensive green roof with the use of grey water for irrigation was designed, built, and tested in experimental operation. In accordance with the principles of circular economy, a substrate for extensive green roofs with an admixture of recycled materials based on recycled demolition waste and pyrolyzed sewage sludge in the form of biochar was designed and initially experimentally tested. The hydrophysical characteristics of the proposed substrate mixtures were determined and two were selected for use on wetland-extensive green roof experimental beds. Water balance, water chemistry at the green roof runoff and vegetation condition were monitored as a function of biochar addition.
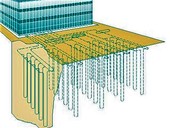
The efficiency of the heat pump also depends on the optimal design of the primary heat collector, most often in the form of a well, a surface collector, but also clinkers or energy baskets. The length of the pipe and its dimensions are closely related to the operating temperature drop in the primary circuit of the heat pump.
A nuclear power plant is a powerful and stable source of electricity. Full replacement of such source with photovoltaics is not easy. We calculated how much PV panels and batteries would be needed for replacement and how much it would cost. The calculation in the article is interactive and the individual calculation parameters can be modified.
The construction industry is the primary source of environmental impacts, especially the carbon footprint. Life cycle assessment (LCA) as an analytical method is used for quantifying the environmental impact of the investigated residential building. Life cycle costs (LCC) from the point of view of the circular economy create an economic model prioritizing reuse and recycling. The aim of this paper is to assess the residential building in terms of carbon footprint, using LCA analysis and circular economy, using LCC analysis. The residential building emits 1 756 tons of CO2e , which represents 41.35 kg CO2e/m2/year. The total estimated life cycle cost of the building in nominal terms is 1 694 699.61 €. This is the average total life cycle cost of 1 995.21 €/m2.
The paper is elaborated in order to outline the understanding of architecture in relation to the environment and to reflect on a systemic conception of the issue of the role of architectural and urban factors in the valuation of buildings. The main task is to determine the progress of the solution method based on the initial research and analysis. A large part of the article is devoted to the explanation and definition of the system of important quantities. The results and findings will serve as a basis for further research.
zpět na aktuální články